Smart Contracts:The Evolution and Impacts

Introduction to Smart Contracts
In 1993, a visionary cryptographer named Nick Szabo conjured up an idea that seemed like science fiction: contracts that could execute themselves, with the terms not written on paper, but in lines of code. Fast forward to today, and this once-futuristic concept, known as smart contracts, is reshaping our digital landscape.
At their heart, smart contracts are more than just a nerdy curiosity. They are automated programs running on blockchain platforms like Ethereum, triggered to action when certain conditions are met. Imagine a world where agreements, complex financial transactions, and even the ownership of digital art are handled not by people, but by unerring lines of code. That’s the realm of smart contracts.
What’s fascinating here is how these digital contracts are challenging our traditional notions of trust and agreement. In the bustling arenas of decentralized finance (DeFi) and digital art, including the burgeoning world of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), smart contracts are the silent power players. They automate, authenticate, and facilitate transactions with a level of efficiency that traditional legal frameworks can’t match.
But it’s not all smooth sailing. The rise of smart contracts brings with it questions about regulation, security, and the very nature of legal agreements in a digital age. Are we ready to accept ‘code as law’? What happens when things go wrong in a world governed by automated contracts?
Evolution of Smart Contracts

The journey of smart contracts from a niche concept to a cornerstone of the blockchain revolution is nothing short of remarkable. In what seems like a blink in the digital age, these contracts have transformed from complex, tech-heavy ideas to essential tools in the ever-expanding realm of blockchain applications.
The real turning point came with platforms like Ethereum. These platforms didn’t just adopt the idea of smart contracts; they turbocharged it. Ethereum, in particular, expanded the capabilities of these contracts far beyond mere transactional functions. Now, they’re not just for the Silicon Valley insiders or cryptography enthusiasts. Today, smart contracts are ubiquitous – a fundamental component in sectors ranging from financial services to supply chain management, from safeguarding intellectual property rights to reshaping legal agreements.
This evolution of smart contracts is a testament to the broader story of digital innovation. It’s a narrative of continuous advancement, mirroring the relentless march of blockchain technology. Each step forward in this technology has broadened the scope and sophistication of smart contracts, making them more accessible, more powerful, and more integral to our digital lives.
But it’s more than just technical evolution. It’s a shift in how we view and interact with the digital world. These contracts are changing the rules of engagement – in how we transact, how we establish trust in the virtual realm, and how we envision the future of digital economies.
Applications and Potential of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are revolutionizing more than just finance; they’re reshaping the very concepts of trust and ownership across numerous industries. In the world of decentralized finance (DeFi), these digital contracts represent more than mere convenience. They stand as pillars of decentralization, sweeping away traditional middlemen and ushering in an era marked by transparency and newfound trust.
In the creative realm, smart contracts are proving to be game-changers. By ensuring the authenticity of intellectual property and automating royalties, they empower artists, granting them unprecedented control over their work. This marks a significant shift towards genuine ownership in the digital world.
The impact on supply chain management is equally transformative. By tracking products from their origin to their final destination, smart contracts inject a level of authenticity and compliance that was previously unattainable. This transparency is laying new foundations of trust in global commerce.
Looking at the public sector, smart contracts hint at a future filled with greater accountability. From streamlining bureaucratic procedures to potentially revolutionizing e-voting systems, they are carving a path towards improved public trust and efficiency.
In essence, smart contracts are more than mere technological innovations. They are the building blocks of a new digital landscape, one where trust, decentralization, authenticity, and ownership are not just envisioned but actively realized.
Smart Contracts by FutuGuard
Empowering Content Creators
FutuGuard’s approach to smart contracts is centered around enhancing user interaction and ownership of digital content. At its core, FutuGuard employs smart contracts to facilitate unique release conditions for content, embodying a philosophy where every interaction becomes more meaningful. Each piece of content on FutuGuard is not just passively consumed but actively engaged with, unlocking its value and relevance through user participation.Each piece of content on FutuGuard, guarded by a pre-defined condition in a smart contract, becomes an interactive experience, released only when these conditions are met. This innovative use of smart contracts ensures a more immersive and dynamic experience, placing content creators and users in control.
In this environment, ownership transcends mere access, becoming a holistic experience of interaction and engagement, driven by the intelligent application of smart contract technology.
FutuGuard's Smart Contract: Engage and Own
Imagine a scenario where FutuGuard applies its smart contract technology to a high-end fashion brand’s product launch. Instead of a traditional reveal, the brand uses FutuGuard to create a series of interactive posts. Each post is tied to a smart contract with conditions like completing a fashion quiz or checking in at designated fashion hotspots. Only upon meeting these conditions is exclusive content or a sneak peek of the new collection released. This method not only engages the audience but also adds a layer of excitement and exclusivity, transforming a standard campaign into an interactive adventure. Through such applications, FutuGuard demonstrates the practical and innovative use of smart contracts in enhancing digital engagement and ownership.
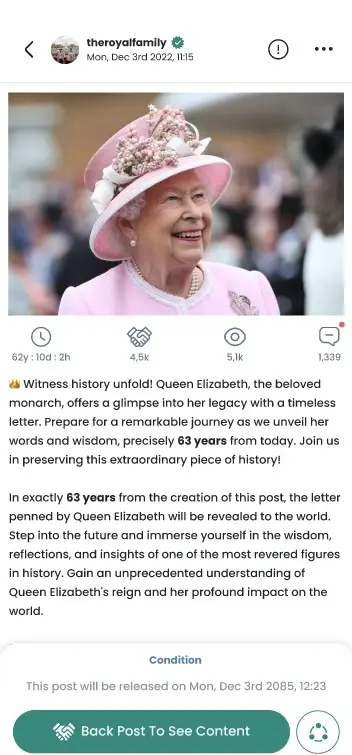
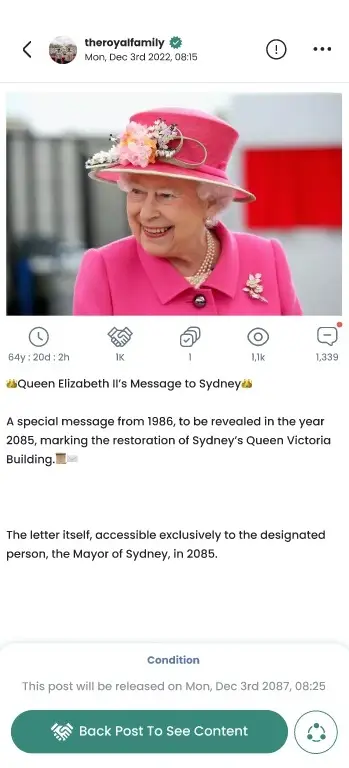
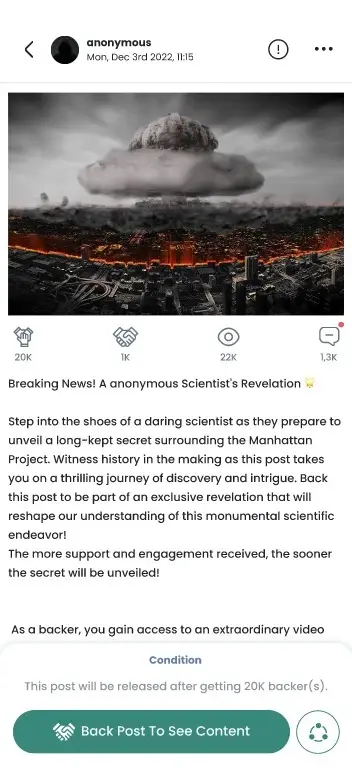
Challenges and Limitations of Smart Contracts

Smart contracts, despite their transformative potential, are accompanied by inherent challenges and limitations. One significant issue is the rigidity of their terms. Smart contracts require precise, objective conditions for execution, making them less adaptable to nuanced or subjective scenarios. Additionally, security concerns are paramount, as any vulnerability in the contract’s code can be exploited, leading to potential losses or unintended consequences.
Moreover, integrating real-world data poses another challenge, as smart contracts cannot natively access off-chain information, relying instead on oracles, which introduce another layer of complexity and potential failure points. These limitations highlight the need for continued innovation and robust security measures in the development and application of smart contracts.

The Future Is Smart Contracts
The future of smart contracts looks promising as they continue to evolve and find new applications across various industries. With advancements in blockchain technology, we can expect smart contracts to become more sophisticated, offering greater flexibility and integrating more seamlessly with real-world data. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) could further enhance their capabilities, allowing for more adaptive and responsive contracts. As these technologies mature, smart contracts are poised to revolutionize not just the financial sector but also fields like supply chain management, intellectual property, and beyond, offering more secure, transparent, and efficient ways of conducting digital transactions and agreements.

Smart Contracts Redefining Agreements
Smart contracts represent a significant shift in how digital agreements and transactions are conducted in the blockchain era. They offer a blend of security, transparency, and automation, fundamentally changing how we approach contracts and digital interactions. While challenges and limitations exist, the ongoing advancements in this technology suggest a bright future. As we continue to witness the growth and application of smart contracts across various sectors, their potential to streamline processes, reduce costs, and foster trust in digital environments becomes increasingly clear. The smart contract, indeed, is set to be a cornerstone in the evolving landscape of digital technology.